How to build a financial forecast in 4 steps? (Tesla Example)

This is a high-level process map for building accurate financial forecasts. If you’re aiming for (or starting in) roles in M&A, FP&A, or PE, understanding financial forecasting is a critical skill.
What steps do you think are most critical in creating a robust forecast?
This guide provides an overview of the steps involved and includes a Tesla case study to bring the concepts to life. For detailed execution of individual steps, explore more articles on our blog.
The Financial Forecasting Process
Forecasting combines historical data, industry trends, and strategic insights to project a company’s future performance. Below is a structured process to create reliable and actionable forecasts:
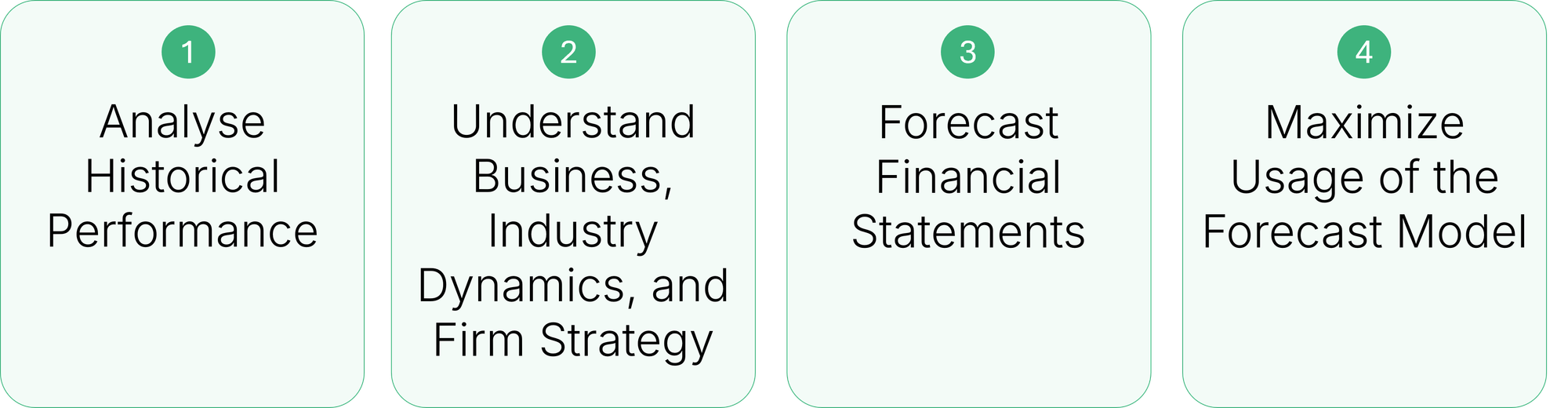
1. Analyze Historical Performance
Understanding a company’s past sets the foundation for future projections.
- Steps:
- Review all line items in the Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss (P&L) statements.
- Differentiate operating, non-operating, and financing items.
- Input financial and non-financial data into a spreadsheet.
- Perform ratio analysis to uncover trends and benchmark against comparable companies or industry averages.
Tesla Example: Analyze Tesla’s financials, noting its rapid revenue growth driven by increased EV sales. Gross margins have improved as production scales, indicating operational efficiencies. Use these insights to compare Tesla’s ratios with competitors like Ford and GM, highlighting its competitive advantage in profitability and growth trajectory.
Key Tip: Historical improvements in Tesla’s gross margins point to scaling production as a key profitability driver.
2. Understand Business, Industry Dynamics, and Firm Strategy
A strong forecast requires a strategic understanding of the company’s position in its industry.
- Steps:
- Gain an understanding of the company’s business and industry.
- Analyze key industry trends and drivers.
- Assess the competitive environment, opportunities, threats, strengths, weaknesses, and strategic plans.
- Identify value drivers and craft a plausible storyline for the forecast.
Tesla Example: Study Tesla’s leadership in the EV market, coupled with rising competition from Rivian and Volkswagen. Consider the industry’s shift toward clean energy and Tesla’s strategic investments in battery technology and global factory expansion. Develop a narrative that these factors will sustain Tesla’s market dominance and profitability.
Key Tip: Align assumptions with Tesla’s strategy of reducing costs through vertical integration and scaling production.

Build resilient forecasts with automated formatting
ProForma is an Excel add-in that smartly color-codes cells to give you an edge in building complex financial models.
3. Forecast Financial Statements
Translate insights into actionable financial projections.
- Steps:
- Use key value drivers from industry and firm-specific trends to guide the forecast.
- Build projections for the P&L, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement.
- Validate forecasts by ensuring they align with the company’s strategy and competitive positioning.
Tesla Example: Forecast Tesla’s revenue growth by estimating EV sales volume and average selling prices (ASP). Assume operating margins improve as Gigafactories achieve greater efficiency. Incorporate planned capital expenditures (capex) to meet production capacity goals, ensuring alignment with Tesla’s growth strategy.
Key Tip: Consider battery cost reductions as a driver of long-term profitability when forecasting Tesla’s margins.
4. Maximize Usage of the Forecast Model
Leverage the forecast model for comprehensive analysis and decision-making.
- Steps:
- Use the model for valuation, capital structure implications, risk analysis, and ratings.
- Perform sensitivity and scenario analyses to understand key output variances.
- Present results in a clear, actionable format for stakeholders.
Tesla Example: Conduct scenario analyses to test the impact of battery cost fluctuations on Tesla’s profitability. Use the model to calculate Tesla’s valuation under different assumptions, such as accelerated EV adoption or delays in factory expansions.
Key Tip: A robust model identifies risks early, such as Tesla’s dependence on raw material costs, enabling proactive strategic planning.

Color-code your forecasting model with one click
ProForma is an Excel add-in that smartly color-codes cells to give you an edge in building complex financial models.
Let's get to building!
Financial forecasting blends technical expertise with strategic insight. By following this structured approach and using real-world examples like Tesla, you can create credible and actionable forecasts to excel in forward-looking finance roles.
What’s the biggest challenge you face when building forecasts? Comment below and share your insights!